Strokes occur without warning, resulting from blood loss to the brain and causing significant damage without immediate treatment. The damage often causes issues with mobility, brain function, and communication, requiring rehab to improve your condition. The most recommended therapies after a stroke include physical, occupational, and speech therapy. The varying treatments offer the best chance of improving function and regaining independence.
Though rehab therapies are used for various medical problems, they are customizable to manage specific conditions. Stroke rehab focuses on the most common stroke symptoms, including the loss of motor skills, balance, mobility, bowels, and speech. The goal is to offer comprehensive care that matches the patient’s needs.
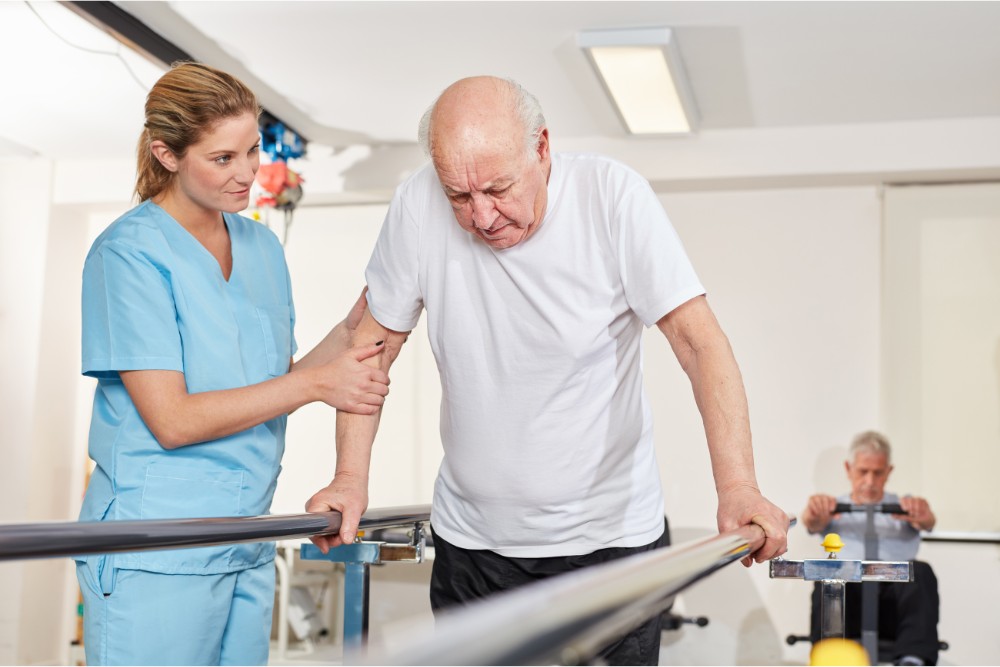

Three Therapies After a Stroke
According to experts, strokes occur at any age but are more common in older adults. The sudden symptoms include weakness in the face or extremities, confusion, vision problems, coordination problems, and difficulty speaking.
Seeking immediate medical attention may prevent long-term damage, but most people require some form of post-stroke rehab. Physical, occupational, and speech therapies are most common, so let’s take a look at what to expect.
Physical therapy
When the brain is deprived of oxygen, motor function is often impaired. You may struggle with mobility and balance. To counter these issues, physical therapy after a stroke is usually required.
The program includes passive and active exercises, resistance training, and gait training. The goal is to rebuild strength and flexibility in the affected limbs. You may also require massage and electrical stimulation to reduce impairment and improve recovery.
Occupational therapy
Another of the vital post-stroke therapies is occupational therapy. The damage done by a stroke often alters fine motor skills used to perform simple daily activities. These include brushing teeth, buttoning clothes, holding a pen, and cooking meals.
A trained therapist assesses your condition and ability to perform these tasks. Then they create a program that teaches you techniques and strategies to relearn lost skills. Home visits determine if aids and equipment are needed to help you move about safely.
Speech therapy
After a stroke, therapies may be required to aid communication, which may be affected in several ways. Aphasia affects talking, understanding others, reading, or writing. Apraxia, dysarthria, and dysphonia also affect speech, causing coordination or weakness in the jaw or vocal cords.
Speech therapists determine the cause of the communication issues and use several techniques to improve those skills. These may include strengthening tongue and mouth exercises, facial movements, word games, and reading aloud.
Other therapies
Depending on your symptoms, your doctor may recommend several therapies after a stroke. Cognitive therapy improves memory, reasoning, judgment, and focus and is often paired with speech therapy.
Since therapies are tailored to the person’s specific needs based on the type and severity of the stroke, there may be a need for psychological therapy. It focuses on providing emotional support to deal with post-stroke anxiety, depression, or frustration.
Another effective treatment of people who have had a stroke is therapeutic recreation activities. Recreational therapy offers fun activities that allow you to socialize, be creative, or get out for some entertainment. It also focuses on engaging hobbies or activities to improve overall well-being. Activities such as yoga and tai chi can be very useful too as they offer relaxation, reduce spasticity and boosts recovery.
Dietary care educates on safe foods for those with swallowing issues and maintaining adequate nutrition. You’ll also learn what foods to avoid to prevent exacerbating your condition and reduce the risk of future strokes.
Other possible rehab services include alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage therapy. Rehab services also offer nursing care, counseling, support groups, or social work.
Resources:
- National Institute on Aging, Stroke: Signs, Causes, and Treatment
https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/stroke/stroke-signs-causes-and-treatment - PubMed Central, Oct. 5, 2022, Effectiveness of Rehabilitation Exercise in Improving Physical Function of Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9566624/ - Stroke Association, Occupational therapy
https://www.stroke.org.uk/stroke/life-after/occupational-therapy - Stroke Foundation, Communication after stroke
https://strokefoundation.org.au/what-we-do/for-survivors-and-carers/after-stroke-factsheets/communication-after-stroke-fact-sheet - Cleveland Clinic, Speech Therapy
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22366-speech-therapy - PubMed Central, Cognitive Rehabilitation Interventions for Post-Stroke Populations
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10494803/ - Stroke Foundation, Diet after stroke
https://strokefoundation.org.au/what-we-do/for-survivors-and-carers/after-stroke-factsheets/diet-after-stroke-fact-sheet - American Stroke Association, Post-Stroke Rehabilitation
https://www.stroke.org/en/life-after-stroke/stroke-rehab/post-stroke-rehabilitation
This content comprises informative and educational resources only and can not be considered as a substitute for professional health or medical guidance. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk. If you have any inquiries or apprehensions about your medical condition or health goals, talk with a licensed physician or healthcare provider.





Leave A Comment