Your brain controls your entire body, so it’s no surprise that mental health issues affect your physical self. However, the reverse is also true, with physical problems altering brain function. When your gut isn’t at its best, mental health issues, such as mood swings or headaches, may arise or worsen. Knowing the symptoms could help your doctor discover the cause of your dilemma.
For instance, when your gut isn’t healthy, you may experience fatigue, brain fog, frequent mood changes, or other neurological issues. Stress and anxiety increase, sleep patterns change, and energy levels drop. If you notice these symptoms, discuss possible causes and treatments with your doctor.
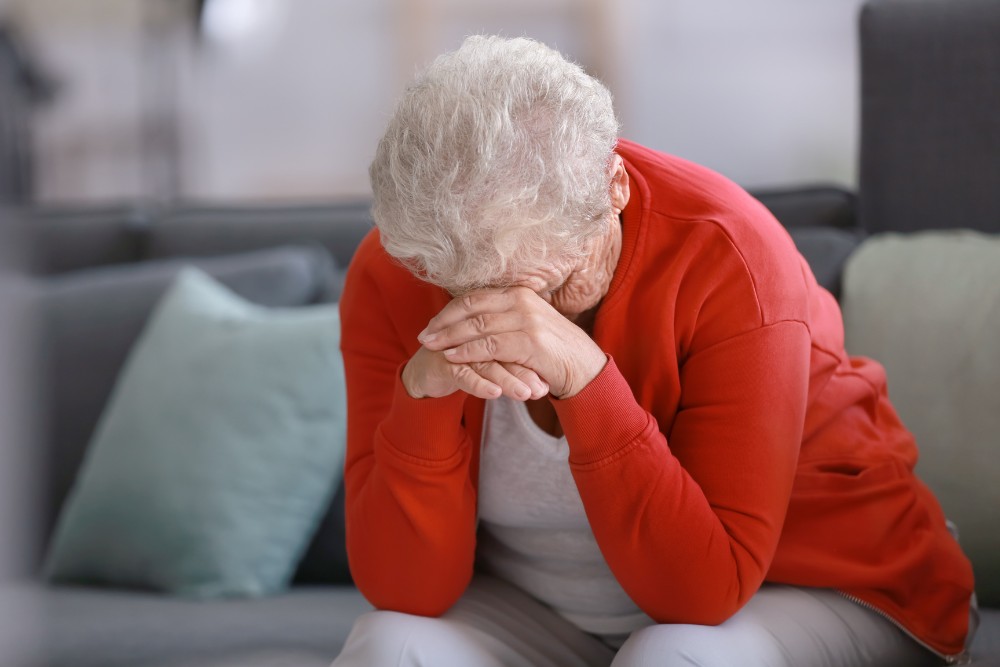

A Troubled Gut Can Affect Your Mental Health
The brain transmits signals throughout the body via the central nervous system. It maintains organ function, cell growth, hormone production, and healing processes.
However, the gut creates several neurotransmitters to send messages to the brain and back. According to experts, the gut microbiome also affects neurological function and mental health. Let’s take a look at the most common issues caused by an unhealthy tummy.
Mood swings
When your stomach is upset, it’s unlikely that you feel happy and social. Though you may think it’s just due to feeling ill, the issue is more complex than most people realize. For instance, several serotonin receptors are located in the gut. When serotonin levels are altered, mood swings often occur.
Consuming unhealthy foods, including fried, fatty, sugary, or salty items, also affects the microbiome. As good and bad bacterial levels change, gut health suffers, as does mental health. Even mood disorders, such as depression, could worsen due to a poor diet and altered hormone levels.
More stress and anxiety
An unhealthy gut may influence mental health by increasing stress and anxiety levels. Studies show changes in gut microbiota alter several hormone levels. The most influential neurotransmitters are serotonin and dopamine. The former is associated with digestion and mood, while the latter is called the feel-good hormone.
According to experts, the microbiome of those with generalized anxiety disorder was less diverse, with reduced richness. They also produced fewer beneficial short-chain fatty acids, with increased unhealthy bacteria. Altering your diet may combat such issues but discuss any changes with your doctor first.
Low energy
Every piece of ingested food is broken down in our stomach and converted into energy. Our bodies use the energy for tissue building, organ function, and healing. Energy is also expended when physically active, requiring higher caloric intake to keep moving.
But physical energy isn’t the only area compromised by poor gut health. Lowered mental energy also results from an altered microbiome. Recent studies show changes in bacteria in the gut are associated with changes to mental energy. Various hormones and proinflammatory cytokines may also increase, reducing energy further.
Poor sleep
Recent evidence shows sleep is another aspect of mental health altered by an unhappy gut. For instance, the Selenomonadales and Negativicutes bacteria in the gut may increase insomnia risks. Higher levels of Ruminococcus torques are linked to snoring. Having too much of various bacteria could also be why night owls stay up later than other people.
Several bacteria in the gut occur naturally, but some are introduced or altered by what we ingest. An unhealthy diet changes the microbiome, affecting your body and mind. Sticking to a diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics maintains gut health and helps you sleep.
Resources:
- Cleveland Clinic, The Gut-Brain Connection
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/the-gut-brain-connection - Harvard Health Publishing, Dec. 7, 2018, Gut feelings: How food affects your mood
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/the-gut-brain-connection - PubMed Central, July 2023, The Role of Gut Microbiota in Anxiety, Depression, and Other Mental Disorders as Well as the Protective Effects of Dietary Components
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10384867/#:~:text=Several%20gut%20microbiota%2C%20especially%20Firmicutes,depression%2C%20and%20other%20mental%20disorders - PubMed Central, Jan. 2022, Trait Energy and Fatigue May Be Connected to gut Bacteria among Young Physically Active Adults: An Exploratory Study
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8839554/ - Sleep Foundation, Oct. 20, 2023, New Study Shows What’s in Your Gut Influences How and When You Sleep
https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-news/gut-microbiome-affects-sleep
This content comprises informative and educational resources only and can not be considered as a substitute for professional health or medical guidance. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk. If you have any inquiries or apprehensions about your medical condition or health goals, talk with a licensed physician or healthcare provider.





Leave A Comment