Our hearts and lungs are the engines of our bodies. Working in tandem, they drive oxygen and nutrients around our organs, allowing us to be active and healthy. Cardiopulmonary rehabilitation refers to efforts to keep the heart and lungs functioning efficiently. A key component of this rehab is physical therapy and exercise.
Let’s dive a little deeper into this all-important area to better understand what this rehab therapy is all about.
What is Cardiopulmonary Rehab?
Cardiopulmonary rehab is for those who may have had a heart attack, angina, heart surgery, or a coronary bypass. The aim of this common rehab program is to get people back on their feet after such an event. It seeks to give people optimal physical function through exercise and education, but also involves comprehensive care.
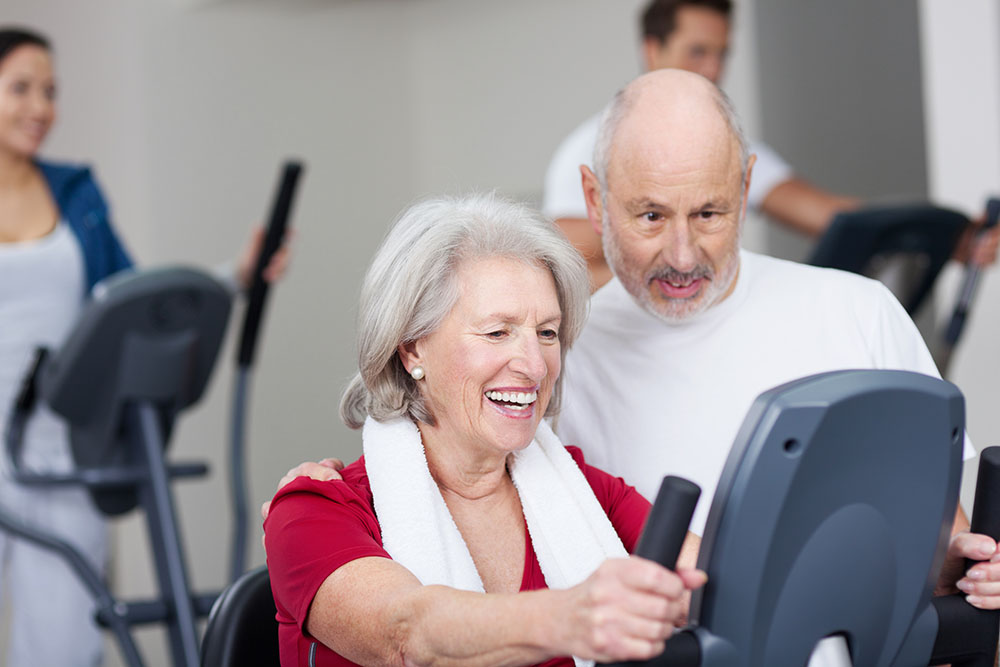

The pulmonary component is designed to help patients with lung-related diseases. These include asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis, or lung cancer. In other words, cardiopulmonary rehab is not only for those who have suffered a heart attack.
As with other forms of rehab, the program helps patients make pro-health lifestyles choices. These may include avoidance of alcohol, giving up smoking, and/or dietary changes. Risk factors for cardiopulmonary problems include obesity, diabetes, stress, and high levels of bad cholesterol. That’s why education is a key part of any cardiopulmonary rehab program.
Are cardio and pulmonary rehab the same?
While cardio and pulmonary rehab are not exactly the same it’s really a question of emphasis. After all, the heart and lungs are closely connected and work together.
Both pulmonary and cardiac rehabilitation help improve quality of life, and increase stamina, strength, and independence. Both may involve gentle aerobic exercises but before these begin a comprehensive evaluation of your overall health is required.
Once a medical professional has devised a personalized program, it may stress the pulmonary or the cardiac side. Either way, light aerobic exercises are likely to be part of your recovery plan.
How does exercise make a difference?
Exercise is a key part of cardiopulmonary rehabilitation and helps strengthen the cardiovascular system and improve its function. A patient case manager carries out tests to determine an appropriate and safe exercise regime. Evaluation of risk factors such as blood pressure and diabetes will help determine the duration and intensity of the exercises.
Regular aerobic exercise can stop or reverse damage to the blood vessels in the heart. Research shows that people who stick with a long-term program of rehab live longer and healthier lives.
Haym Salomon Home for Nursing and Rehabilitation in Brooklyn NY and its top-quality specialists understand the stress that heart and lung problems cause. Therefore, as well as professional care, our cardiopulmonary rehabilitation program includes much-needed emotional support in a warm and friendly environment.
Do contact us or walk in any time to talk to us and see things for yourself. Ask us any questions you may have. We are here to help and answer any concerns you may have.
This content comprises informative and educational resources only and can not be considered as a substitute for professional health or medical guidance. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk. If you have any inquiries or apprehensions about your medical condition or health goals, talk with a licensed physician or healthcare provider.





Leave A Comment